In a world where data breaches, identity theft, and cyberattacks are becoming increasingly common, the need for stronger digital security has never been greater. This is where blockchain technology comes into the picture.
Often associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain is much more than digital money. It is a secure, decentralized, and transparent system for storing and transferring information online. From banking and healthcare to cybersecurity and the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain is reshaping how digital trust is built.
This beginner-friendly guide explains what blockchain technology is, how it works, why it’s secure, its advantages, limitations, and what the future holds—all in simple, easy-to-understand language.
🔎 What Is Blockchain Technology? (Beginner Explanation)
Blockchain technology is a digital record-keeping system that stores information across a distributed network of computers instead of a single central server.
Unlike traditional databases:
- Data is not controlled by one authority
- Records are immutable (cannot be changed easily)
- Transactions are transparent and verifiable
Blockchain stores every transaction in a block and connects each block in sequence, creating a secure chain of records.
👉 In simple words: Blockchain is a shared digital ledger that records data securely, transparently, and permanently.
⚙️ How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
To understand how blockchain works, let’s break it down step by step.
1️⃣ Transaction Initiation
A user initiates a transaction—such as sending cryptocurrency, sharing data, or recording ownership.
2️⃣ Transaction Verification
The transaction is broadcast to a decentralized network of computers (nodes), where it is verified using predefined rules.
3️⃣ Block Creation
Once verified, the transaction is grouped with others into a block containing:
- Transaction data
- Timestamp
- Cryptographic hash
- Reference to the previous block
4️⃣ Block Validation
The block is validated using a consensus mechanism (explained below).
5️⃣ Block Added to the Chain
After validation, the block is permanently added to the blockchain and distributed across the network.
✔️ The data becomes tamper-resistant and publicly verifiable.
🧱 Core Components of Blockchain Architecture
🔹 Blocks
Blocks store transaction data and metadata. Each block includes a cryptographic hash linking it to the previous block.
🔹 Chain
The chain ensures data continuity and integrity. Altering one block would require changing every subsequent block—nearly impossible.
🔹 Nodes
Nodes are independent computers that maintain and validate copies of the blockchain.
🌐 Blocks, Chains, and Decentralization Explained
Traditional systems rely on centralized servers, which create a single point of failure. Blockchain eliminates this risk through decentralization.
Key benefits of decentralization:
- No single authority controls data
- No central failure point
- Increased resistance to hacking
- Higher transparency and trust
This structure makes blockchain extremely resilient against cyberattacks.
🔐 Consensus Mechanisms: Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake
Consensus mechanisms ensure all participants agree on the validity of transactions.
⚙️ Proof of Work (PoW)
- Used by Bitcoin
- Requires solving complex mathematical puzzles
- Highly secure but energy-intensive
🌱 Proof of Stake (PoS)
- Used by Ethereum 2.0 and newer blockchains
- Validators are chosen based on staked assets
- More energy-efficient and scalable
👉 In 2026, PoS and hybrid models are becoming the industry standard due to sustainability concerns.
🛡️ Blockchain’s Role in Digital Security & Cybersecurity
How Blockchain Enhances Online Security
Blockchain improves cybersecurity through:
- Cryptographic encryption
- Immutability of records
- Decentralized storage
- Consensus-based validation
Once data is recorded, it cannot be altered without network approval—dramatically reducing fraud and unauthorized changes.
🔏 Benefits of Decentralization & Encryption
- Eliminates single-point failures
- Prevents unauthorized data modification
- Protects sensitive user information
- Enhances identity verification systems
This makes blockchain ideal for financial transactions, identity management, and secure data sharing.
🌍 Real-World Applications of Blockchain in Cybersecurity
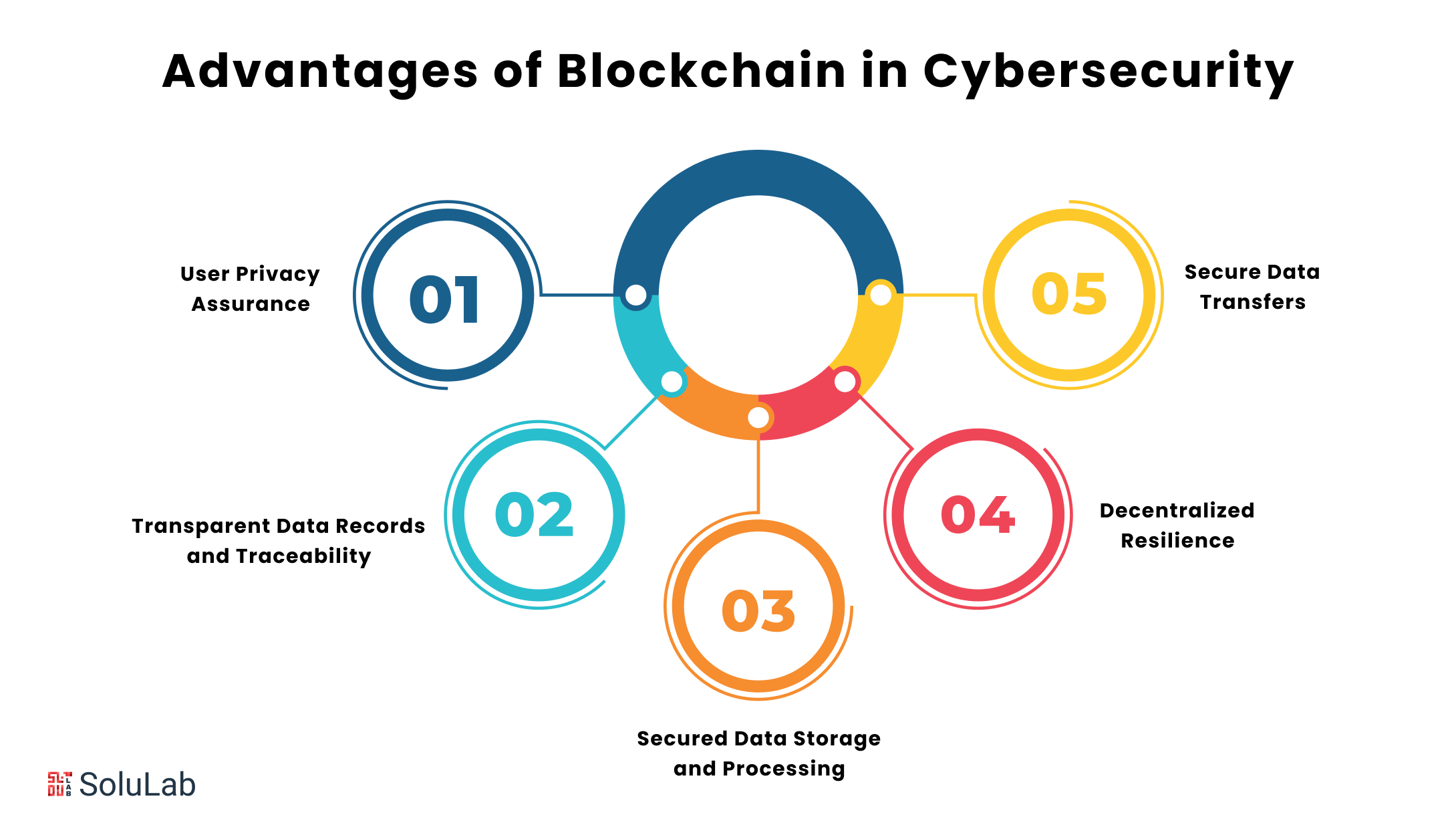
Blockchain is already being used in:
- Supply Chain Security – Prevents counterfeit products
- Digital Identity Protection – Self-sovereign identities
- Healthcare Data Security – Tamper-proof patient records
- Voting Systems – Transparent and fraud-resistant elections
- Enterprise Cybersecurity – Secure access control systems
✅ Advantages of Blockchain Technology
Key Benefits
- Enhanced data security
- High transparency
- Reduced fraud risks
- Lower operational costs
- No need for intermediaries
Why Businesses Are Adopting Blockchain
- Faster transactions
- Reduced trust dependency
- Improved compliance tracking
- Stronger auditability
❌ Limitations & Challenges of Blockchain Adoption

Despite its benefits, blockchain still faces challenges:
⚠️ Major Limitations
- High energy consumption (PoW systems)
- Scalability constraints
- Regulatory uncertainty
- Integration with legacy systems
Ongoing innovations such as Layer-2 scaling and regulatory frameworks aim to address these issues.
🔮 Future of Blockchain Technology
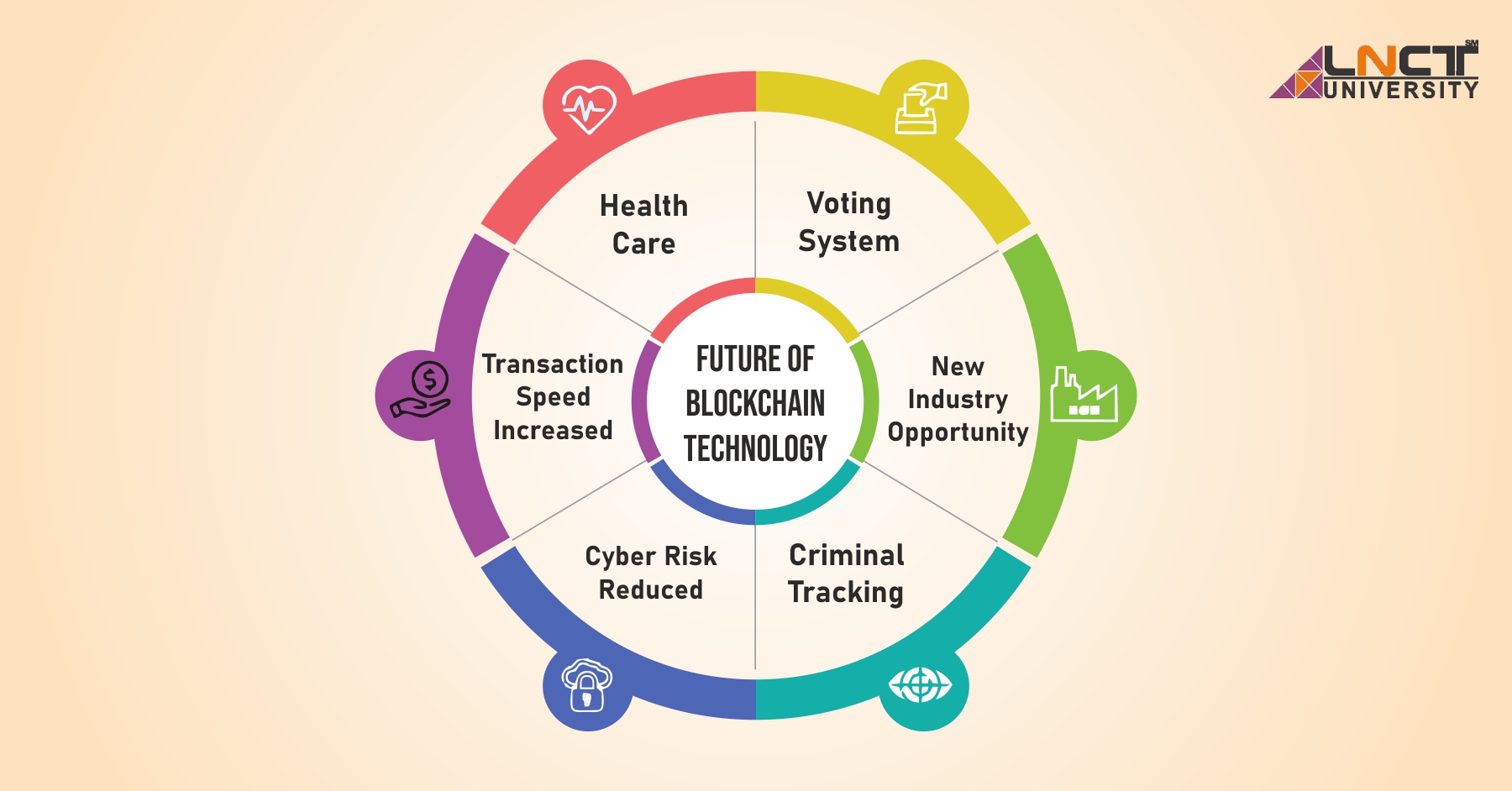
How Blockchain Is Shaping Future Trends
Blockchain is expected to play a key role in:
- Digital identity systems
- Decentralized finance (DeFi)
- Web3 infrastructure
- Secure AI data sharing
🤖 Blockchain and the Internet of Things (IoT)
Blockchain can secure IoT networks by:
- Verifying device identities
- Protecting sensor data
- Preventing unauthorized access
This combination enables secure automation and smart ecosystems.
🌱 The Potential for Widespread Adoption
As scalability improves and regulations mature, blockchain adoption is expected to accelerate across industries globally.
Despite its advantages, blockchain faces challenges, including high energy consumption, scalability issues, and regulatory concerns that may slow widespread adoption.
- Energy Consumption, Regulatory Concerns, and Scalability Issues ❌: Blockchain systems like Bitcoin require significant computational power, raising concerns about energy usage. Regulatory and scalability challenges also hinder adoption.
❓ FAQs – Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a secure digital ledger that records data in blocks linked together, making it very difficult to alter or hack.
Public, private, and consortium blockchains—each designed for different use cases.
No. Blockchain is widely used in cybersecurity, healthcare, supply chains, finance, and IoT.
Yes. Blockchain uses encryption, decentralization, and consensus to ensure high security.
Blockchain will power Web3, secure digital identities, IoT, and next-generation cybersecurity systems.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is redefining digital trust, security, and transparency. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, blockchain offers a powerful foundation for secure digital systems.
Understanding what blockchain technology is and how it works is no longer optional—it’s essential for navigating the future of the digital world.
Hi, I’m Aditya Rathod, a tech content creator and the founder of Zynicon.com.
At Zynicon, I publish clear, practical, and experience-driven content focused on technology, apps, gadgets, AI tools, and emerging digital trends. My goal is to simplify fast-evolving tech topics and present them in a way that is easy to understand, reliable, and genuinely helpful for both beginners and tech enthusiasts.
I actively explore new tools, test apps and devices, and research digital features to ensure every guide and tutorial is written manually, fact-checked, and based on real-world usage. Rather than using hype or jargon, I focus on clarity, accuracy, and usefulness so readers can make informed decisions with confidence.
Through Zynicon, I aim to build a trusted knowledge platform where users can stay updated with technology, discover useful solutions, and learn at their own pace—without confusion or misleading information.
Thank you for being part of the Zynicon community and taking the time to read my work.
Choice of Lineage 2 server to start in the game
L2 X5.
Secrets of the durability of double glazed windows in Melbourne
double glazing melbourne
Выгодные предложения на технику Microsoft, помогут сэкономить ваш бюджет.
разработка на power platform .